VNA Noise Analysis¶
This example records a series of sweeps from a VNA to touchstone files, named in a chronological order. These are then used to characterize the noise of a VNA.
Touchstone File Retrieval¶
import skrf as rf
import os,datetime
nsweeps = 101 # number of sweeps to take
dir = datetime.datetime.now().date().__str__() # directory to save files in
myvna = rf.vna.HP8720() # HP8510 also available
os.mkdir(dir)
for k in range(nsweeps):
print k
ntwk = myvna.s11
date_string = datetime.datetime.now().__str__().replace(':','-')
ntwk.write_touchstone(dir +'/'+ date_string)
myvna.close()
Noise Analysis¶
Calculates and plots various metrics of noise, given a directory of touchstone files, as would be created from the previous script.
import skrf as rf
from pylab import *
dir = '2010-12-03' # directory of touchstone files
npoints = 3 # number of frequency points to calculate statistics for
# load all touchstones in directory into a dictionary, and sort keys
data = rf.load_all_touchstones(dir+'/')
keys=data.keys()
keys.sort()
# length of frequency vector of each network
f_len = data[keys[0]].frequency.npoints
# frequency vector indecies at which we will calculate the statistics
f_vector = [int(k) for k in linspace(0,f_len-1, npoints)]
#loop through the frequencies of interest and calculate statistics
for f in f_vector:
# for legends
f_scaled = data[keys[0]].frequency.f_scaled[f]
f_unit = data[keys[0]].frequency.unit
# z is 1d complex array of the s11 at the current frequency, it is
# as long as the number of touchsone files
z = array( [(data[keys[k]]).s[f,0,0] for k in range(len(keys))])
phase_change = rf.complex_2_degree(z * 1/z[0])
phase_change = phase_change - mean(phase_change)
mag_change = rf.complex_2_magnitude(z-z[0])
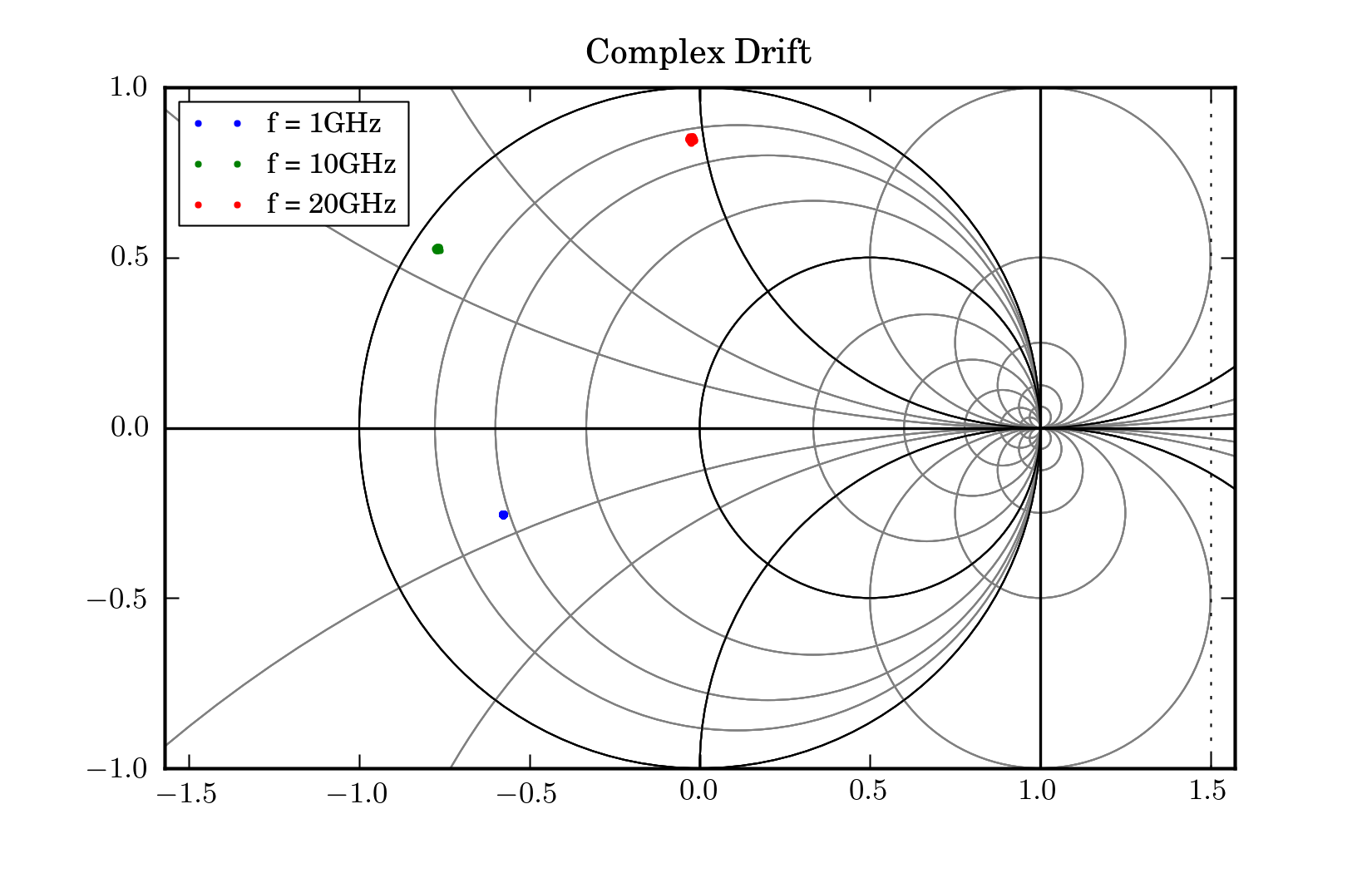
figure(1)
title('Complex Drift')
plot(z.real,z.imag,'.',label='f = %i%s'% ( f_scaled,f_unit))
axis('equal')
legend()
rf.smith()
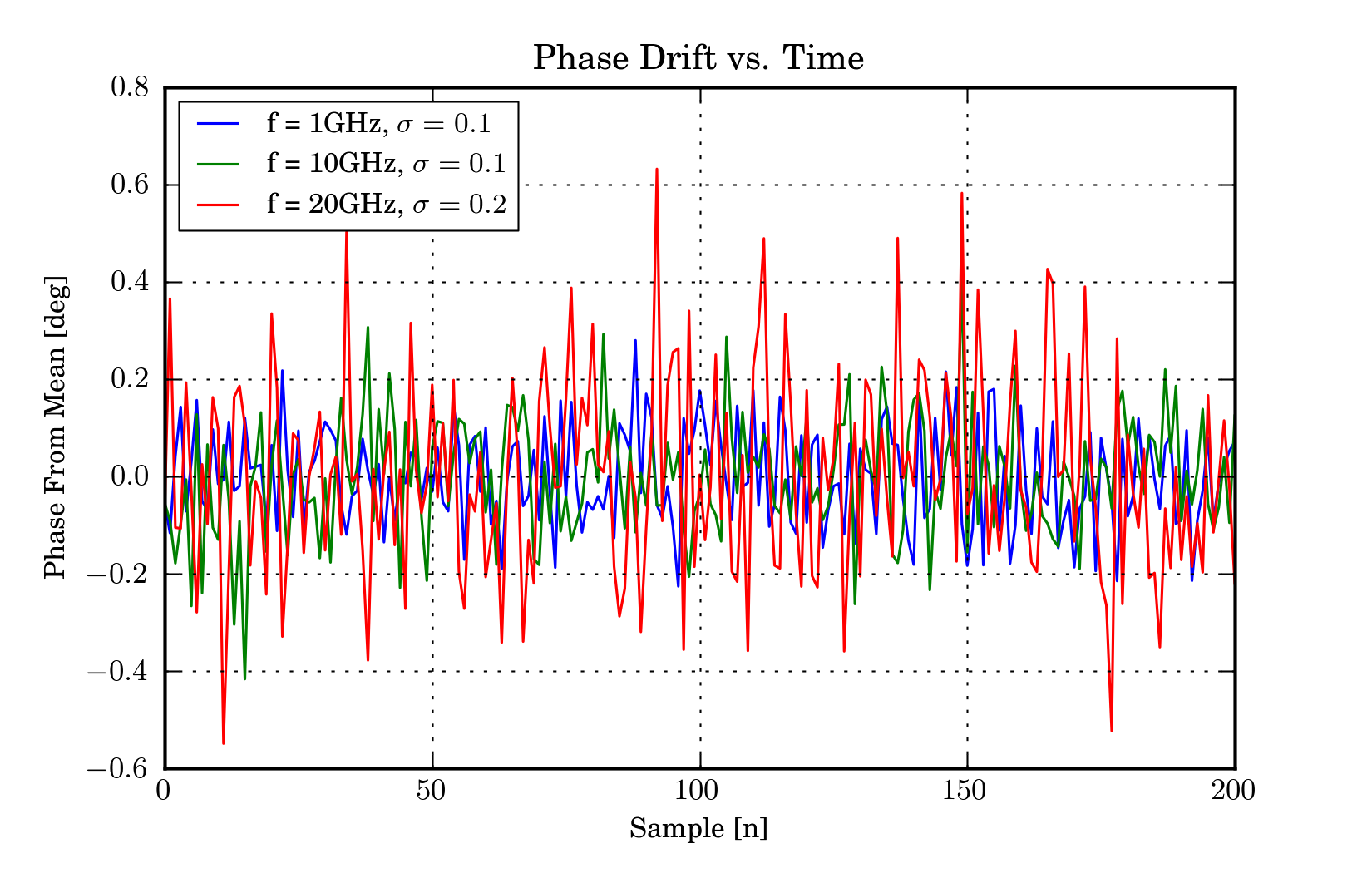
figure(2)
title('Phase Drift vs. Time')
xlabel('Sample [n]')
ylabel('Phase From Mean [deg]')
plot(phase_change,label='f = %i%s, $\sigma=%.1f$'%(f_scaled,f_unit,std(phase_change)))
legend()
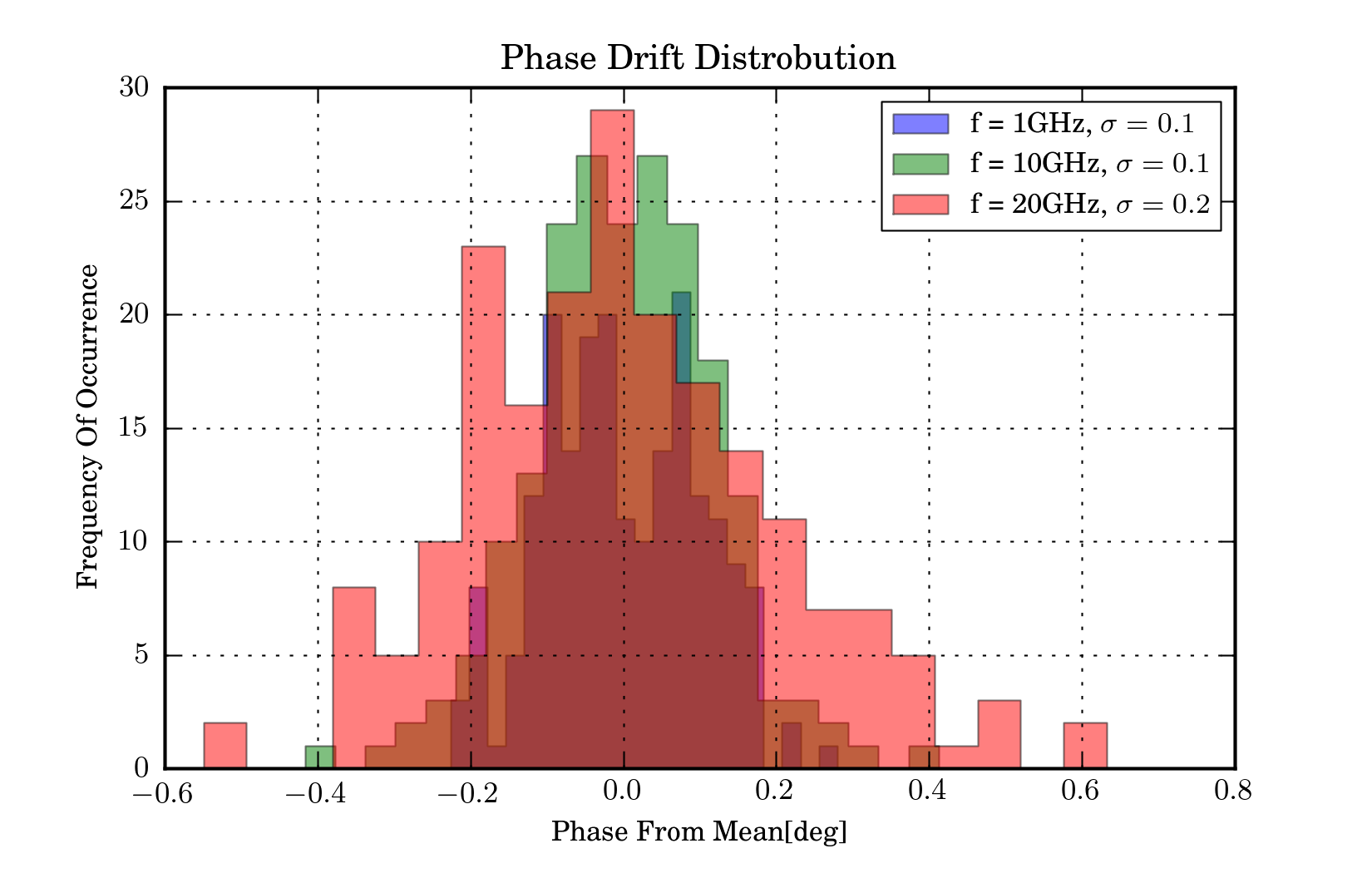
figure(3)
title('Phase Drift Distribution')
xlabel('Phase From Mean[deg]')
ylabel('Frequency Of Occurrence')
hist(phase_change,alpha=.5,bins=21,histtype='stepfilled',\
label='f = %i%s, $\sigma=%.1f$'%(f_scaled,f_unit,std(phase_change)) )
legend()
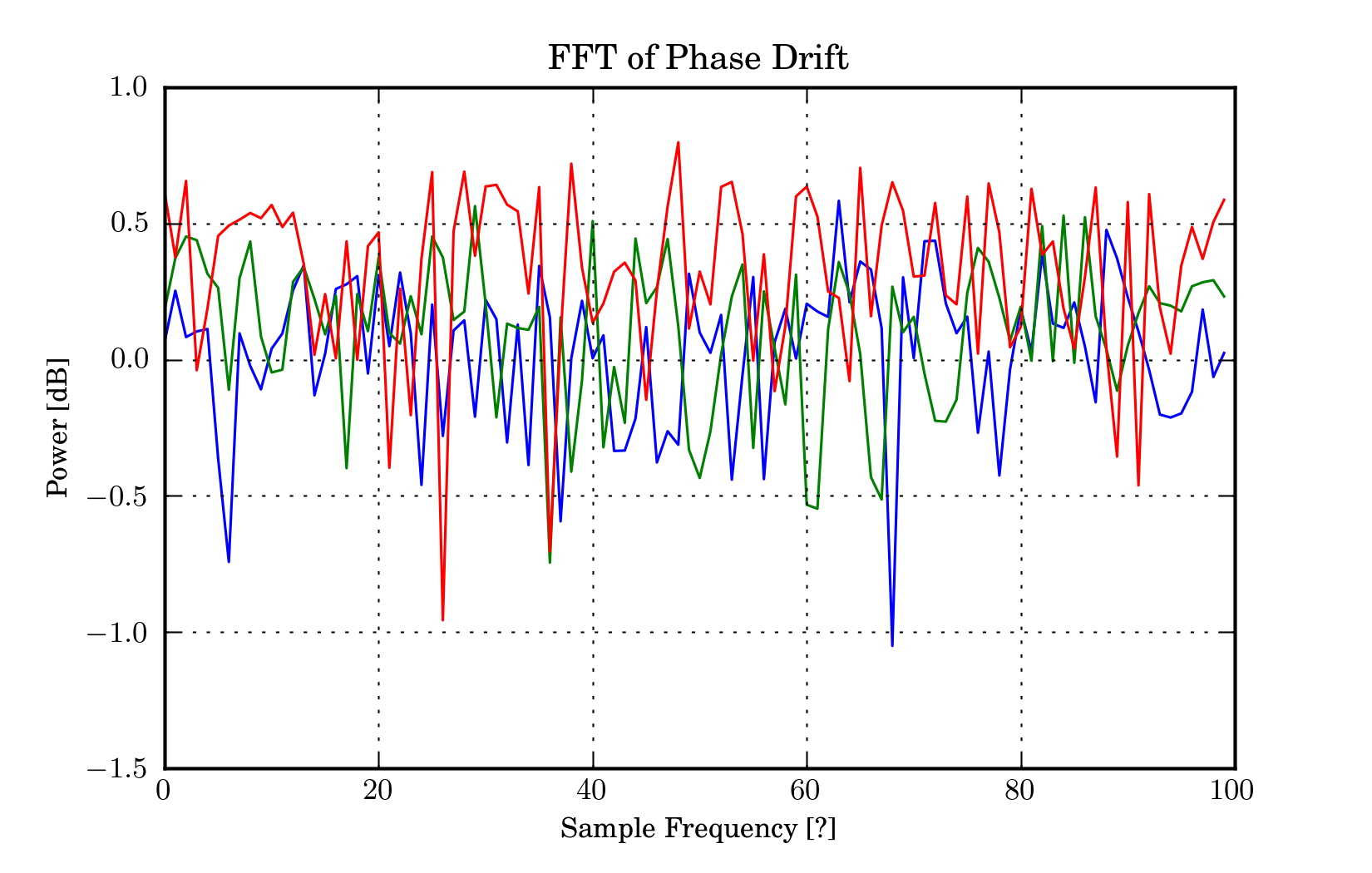
figure(4)
title('FFT of Phase Drift')
ylabel('Power [dB]')
xlabel('Sample Frequency [?]')
plot(log10(abs(fftshift(fft(phase_change))))[len(keys)/2+1:])
draw();show();